Solution comes with actions;
actions implies choices and decisions;
decisions need a rationale;
(anyway Gideon says: act immediately)
The first element of a Decision Problem are:
WHO, HOW, WHAT
Who takes decision
Who is involved in the decision process
Who is impacted by the decision
How decision are taken? (which criteria I’ll use)
What is the objective?
Sometime the objective and the method are clear (puzzle problem);
Sometime the objective is clear but the method is not (the problem);
Sometimes nothing is clear (meaning you look for trebles).
Depending on the situation we can have optimal solution (substantial rationality)
or just a satisfactory solution (Procedural rationality).
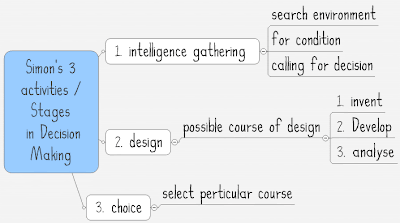
Herbert Alexander Simon (June 15, 1916– February 9, 2001) is the father of decision making theory. Baruk abba chaver! He says: i.e. it is impossible to have perfect and complete information at any given time to make a decision.
In decision-making, Simon believed that agents face uncertainty about the future and costs in acquiring information in the present. These factors limit the extent to which agents can make a fully rational decision, thus they possess only “bounded rationality” and must make decisions by “satisficing,” or choosing that which might not be optimal but which will make them happy enough
The task of rational decision making is to select the alternative that results in the more preferred set of all the possible consequences of actions. This task can be divided into three required steps: (1) the identification and listing of all the alternatives; (2) the determination of all the consequences resulting from each of the alternatives; and (3) the comparison of the accuracy and efficiency of each of these sets of consequences.
(decision, action, consequences).
The correctness of decisions is measured by two major criteria: (1) adequacy of achieving the desired objective; and (2) the efficiency with which the result was obtained. Many members of the organization may focus on adequacy, but the overall administrative management must pay particular attention to the efficiency with which the desired result was obtained.
Ok, that’s all about Simon
There are another couple of things to mention:
Getting information: be satisfied with the minimum, in this case! and think about Pareto.
Participatory approach: it helps to get better info about the problem and the possible solution
It makes the solution more acceptable by stakeholders.
There are risks
Decisions must be: Transparent; Explicit, Clear.
(anyway Gideon says: act immediately)
The first element of a Decision Problem are:
WHO, HOW, WHAT
Who takes decision
Who is involved in the decision process
Who is impacted by the decision
How decision are taken? (which criteria I’ll use)
What is the objective?
Sometime the objective and the method are clear (puzzle problem);
Sometime the objective is clear but the method is not (the problem);
Sometimes nothing is clear (meaning you look for trebles).
Depending on the situation we can have optimal solution (substantial rationality)
or just a satisfactory solution (Procedural rationality).
Herbert Alexander Simon (June 15, 1916– February 9, 2001) is the father of decision making theory. Baruk abba chaver! He says: i.e. it is impossible to have perfect and complete information at any given time to make a decision.
In decision-making, Simon believed that agents face uncertainty about the future and costs in acquiring information in the present. These factors limit the extent to which agents can make a fully rational decision, thus they possess only “bounded rationality” and must make decisions by “satisficing,” or choosing that which might not be optimal but which will make them happy enough
The task of rational decision making is to select the alternative that results in the more preferred set of all the possible consequences of actions. This task can be divided into three required steps: (1) the identification and listing of all the alternatives; (2) the determination of all the consequences resulting from each of the alternatives; and (3) the comparison of the accuracy and efficiency of each of these sets of consequences.
(decision, action, consequences).
The correctness of decisions is measured by two major criteria: (1) adequacy of achieving the desired objective; and (2) the efficiency with which the result was obtained. Many members of the organization may focus on adequacy, but the overall administrative management must pay particular attention to the efficiency with which the desired result was obtained.
Ok, that’s all about Simon
There are another couple of things to mention:
Getting information: be satisfied with the minimum, in this case! and think about Pareto.
Participatory approach: it helps to get better info about the problem and the possible solution
It makes the solution more acceptable by stakeholders.
There are risks
Decisions must be: Transparent; Explicit, Clear.
No comments:
Post a Comment