.jpg)
Impact of climate change
Impact of adaptation strategies
Does not matter whether climate change is anthropogenic or not… it is a fact anyway. There are three ways to walk now: we adapt; we mitigate it; we ignore it.. (I’ll do them all together ;)
Business as usual does not require new thinking, but adaptation and mitigation strategies do and we may need modelling for that.What does a model do: it is a simplification of the system, it tells me how all the element of system moves together.
When there resources we are dealing with are scarce, that’s an economic model.
When there is a cost benefit analysis that’s an economic model.
When there are infinite resources to be allocate that’s not an economic model.
An ideal policy would combine both adaptation and mitigation.
Modelling stages:
10) measuring impact of CC on welfare;
20) measuring costs&benefits of different adaptation&mitigation strategies;
Strategies? How would you judge them?
10) effectiveness: ability to reach the goal (yes/no; %)
20) efficiency: ability to reach the goal at a minimal cost ($)
30) equity: related to resource allocation;
The chain of events in a CC model:
10) climate system dynamics or scenarios will impact on (20)
20) environmental dynamics will impact on (30)
30) social and economic dynamics will impact on (10)
apparently we always look at the changes in the system… the delta in the agricultural costs, delta in soil productivity, delta in water availability etc etc… mind the delta! Sure..
Rotmans and Dowlatabady 1995
Models have plenty of gaps, here they are in two macro groups:
10) incompleteness: we don’t know data or don’t understand relations (who doesn’t anyway?)
20) Probability: we are not certain of data and relation and there is a probability distribution attached to a certain event or estimation. Discount choice
We know a lot about costs of adaptation and mitigation we don’t know enough about their benefit. Benefits are probable, cost are certain….
Moreover many investments and many natural phenomena are not reversible, for example a dike cannot be dismantled and reused somewhere else (yet); a species extinction is even a more sad story.
Welfare measurement and redistribution always imply ethical judgement, and also decision about..
- Inter-generations distribution (temporal distribution)
- Infra-generations distribution (spatial distribution)
Moreover, it is possible to rank welfare level in a cardinal order but it is not possible to measure how much a person or a group is better well off the another.
The following are three possible objective functions, were:
W is welfare, a is a weight, α is the interest rate..
.jpg)
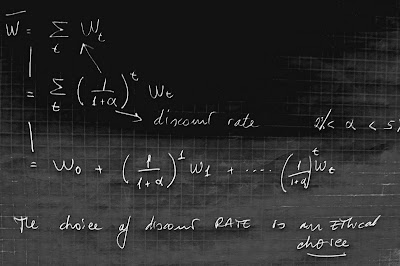.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment